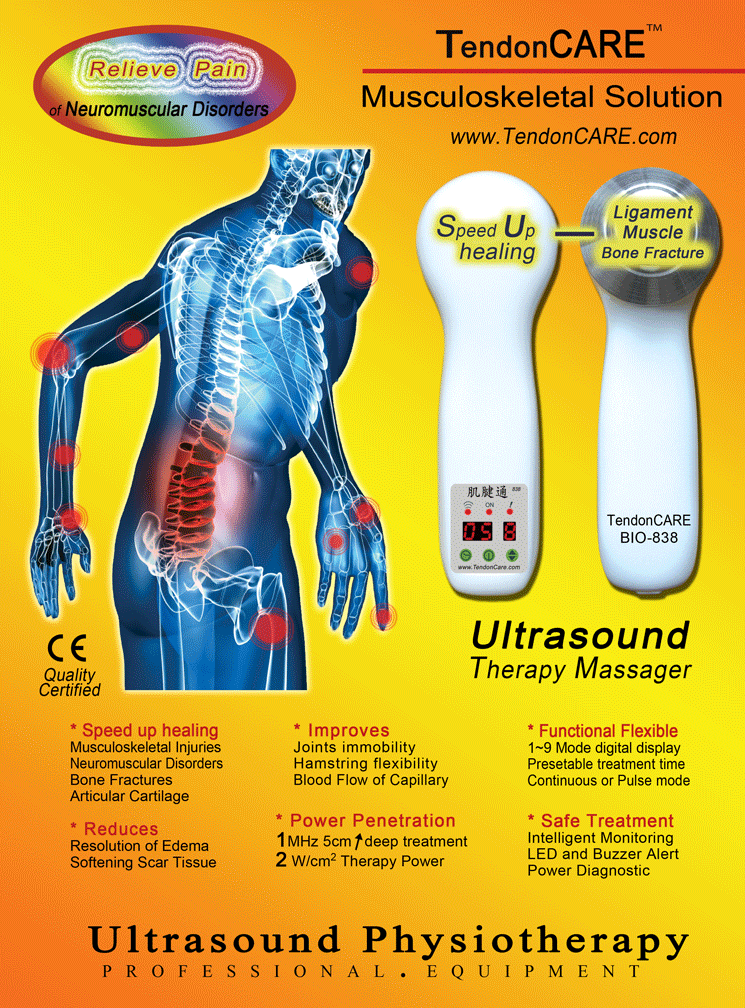
Specification:
Please refer to English version
Ultrasound is a very good form of treatment for soft tissue injuries, such as joint and muscle sprains, bursitis and tendonitis. It is often used by physical therapists, trainers, and many other healthcare providers. A very high frequency 1MHz (100,0000Hz) sound waves vibrate tissues deep inside the injured area and creates thermal, mechanical and chemical effects.
Thermal effects include deep tissue heating at depths to 5cm or more. The
thermal effects of ultrasound differ from diathermy (the use of electrical
impulses to produce generalized vasodilatation) in that the ultrasound beam
heats only a small tissue area that approximates the cross-section of the
beam. This heating effect is concentrated in muscles, ligaments, nerves,
bones, and where the ultrasound beam crosses from one type of tissue to
another.
The mechanical effects are best described as micro-massage, a deep stirring action within the tissue. The benefit of this action is increased circulation to the damaged tissue. In addition, ultrasound is capable of separating collagen fibers from one another and of changing the tensile strength of tendons, thereby increasing their extensibility.
The physiological benefits from ultrasound therapy are numerous. Ultrasound
therapy affects the peripheral nerves by chemically changing the conduction
velocity (this has been shown clinically in situ). Ultrasound alters the
diffusion of Na+ and K+(sodium and potassium) across red blood cell membranes.
Ultrasound can also remove some salt deposits from irritated tissues.
Search keys: LIPUS device - Pulsed Shockwave device - Protein Synethsis
Accelerator -
Ultrasound therapy device - Bone Growth Stimulator - bone fracture healing